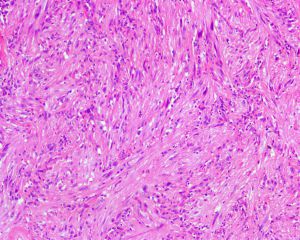
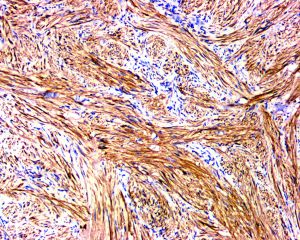
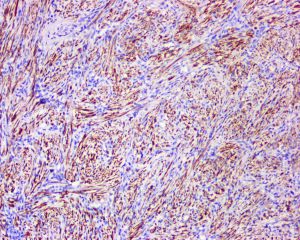
1、主要发生于中年人;有两种类型:一种为躯体深部软组织平滑肌瘤,另一种为盆腔腹膜后/腹腔平滑肌瘤;
2、界限清楚,平均直径7.7cm;
3、瘤细胞类似成熟的平滑肌细胞,部分区域肿瘤排列丰富密集,部分疏松水肿,肿瘤细胞梭形,呈编织束状排列;
4、瘤细胞形态温和,含有丰富、嗜伊红色的胞质,核两端平钝或呈雪茄样,核末端常见核旁空泡,核无异型性,核分裂象罕见(<1/50HPF),女性腹膜后病变核分裂象可达5/50HPF;
5、部分病例内可见变性或退行性变,如纤维化、玻璃样变、钙化和黏液变;但不见凝固性坏死;
6、如有明显脂肪改变则应称为肌脂肪瘤;
7、局灶退性变和非典型性的意义尚不明确,应仔细寻找分裂像并进一步取材。
1、神经鞘瘤:有Antoni A和Antoni B结构,常出血、囊性变;瘤细胞S100(+);
2、纤维瘤病:边界不清,侵袭性生长;瘤细胞β-catenin(+);
3、炎性肌纤维母细胞性肿瘤:属中间性肿瘤,轻度异型的梭形瘤细胞呈编织状排列,背景见大量淋巴细胞、浆细胞和组织细胞浸润;ALK(+),SMA灶性(+);
4、胃肠外胃肠间质瘤:较少见,瘤细胞呈梭形,排列的形态复杂多样;CD117、CD34、DOG-1(+)。
1.Miettinen M: Smooth muscle tumors of soft tissue and non-uterine viscera: biology and prognosis. Mod Pathol. 27 Suppl 1:S17-29, 2014
2.Miettinen M et al: Evaluation of biological potential of smooth muscle tumours. Histopathology. 48(1):97-105, 2006
3.Hornick JL et al: Criteria for malignancy in nonvisceral smooth muscle tumors. Ann Diagn Pathol. 7(1):60-6, 2003
4.Weiss SW: Smooth muscle tumors of soft tissue. Adv Anat Pathol. 9(6):351-9, 2002
5.Billings SD et al: Do leiomyomas of deep soft tissue exist? An analysis of highly differentiated smooth muscle tumors of deep soft tissue supporting two distinct subtypes. Am J Surg Pathol. 25(9):1134-42, 2001