疾病名称:
肌内黏液瘤
作者:
赵明 刘正智
英文名称:
Intramuscular Myxoma
发病部位:
大腿、肩、臀、上臂、头颈部、胸壁和小腿
诊断要点:
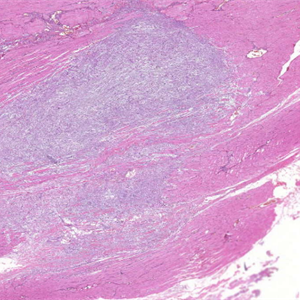
1. 好发于中老年女性(40-70岁),多见于大腿、肩、臀、上臂,常表现为肌肉内孤立性的无痛性肿块,卵圆形或球形,胶冻样,少数可有多个肿块,与Carney综合征或Mazabraud综合征有关,后者常伴有骨纤维结构不;
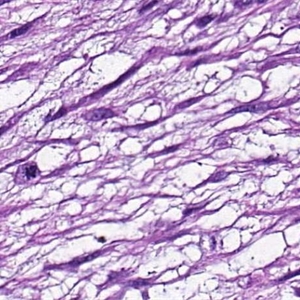
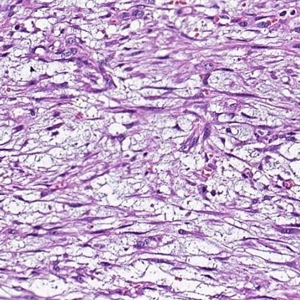
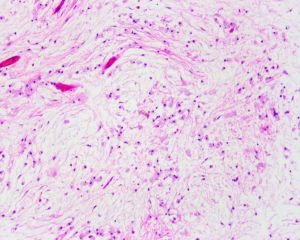
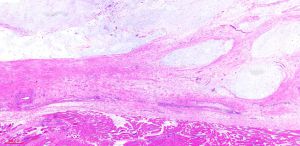
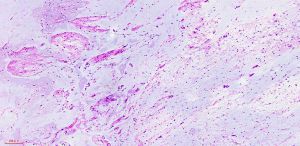
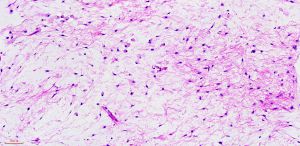
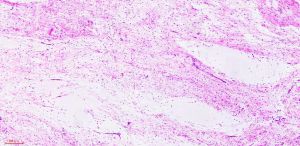
2. 镜下见在大量黏液性背景上稀疏散在分布着小的卵圆形、梭形、星芒状细胞;
3. 细胞胞质少而不清,含有多个纤细的细胞突起,核小,固缩状,深染,不见核仁;
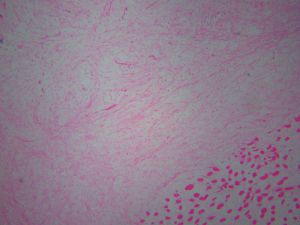
4. 细胞间为疏松的网状纤维网,基质内的黏液阿辛蓝、黏液卡红和胶体铁染色阳性,可被透明质酸酶消化,可见多少不等的泡沫样组织细胞聚集,血管较稀疏,中央可见黏液性囊肿;
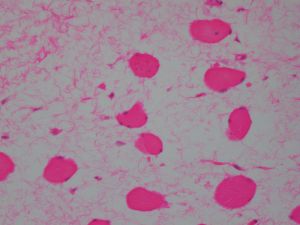
5. 病变的周边区域常见散在萎缩性肌纤维;
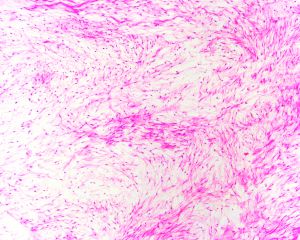
6. 部分病例部分区域细胞丰富,间质内可见较多的胶原纤维,但细胞无异型性,也不见核分裂像,可称为富于细胞性黏液瘤。
图片:
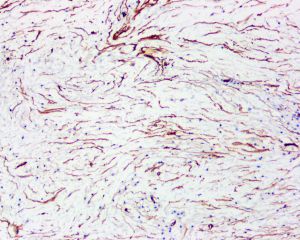
免疫组织化学染色:
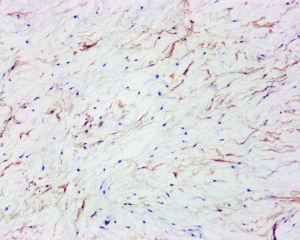
梭形细胞vimentin阳性,S-100阴性,可不同程度表达CD34、desmin和actin。
分子标记:
60%左右存在GNAS1基因突变
鉴别诊断:
黏液性脂肪肉瘤:血管呈鸡爪样丛状排列,可见脂肪母细胞。遗传学上特征性的表现为DDIT3基因易位。
低级别黏液纤维肉瘤:可见肿瘤细胞围绕弯曲的血管生长,瘤细胞至少可见局灶的多形性,散在的假脂肪母细胞以及核分裂象。遗传学上无GNAS1基因突变。
预后:
良性,罕见复发。富于细胞的病例亦表现为惰性进程。
治疗:
完整切除
参考文献:
Delaney D, Diss TC, Presneau N, et al. GNAS1 mutations occur more commonly than previously thought in intramuscular myxoma. Mod Pathol 2009;22(5):718–24.
Nielsen GP, O’Connell JX, Rosenberg AE. Intramuscular myxoma: a clinicopathologic study of 51 cases with emphasis on hypercellular and hypervascular variants. Am J Surg Pathol 1998;22(10):1222–7.
van Roggen JF, McMenamin ME, Fletcher CD. Cellular myxoma of soft tissue: a clinicopathological study of 38 cases confirming indolent clinical behaviour. Histopathology 2001;39(3):287–97.