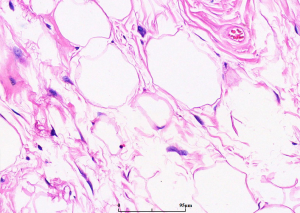
非典型脂肪瘤性肿瘤
Atypical Lipomatous Tumor
刘正智
发布时间:2016-07-27 13:01:08
同义词(或曾用名):高分化脂肪肉瘤、非典型脂肪瘤、多形性脂肪瘤、硬化性脂肪肉瘤、脂肪瘤样脂肪肉瘤、
概述:
发病部位:好发于大腿,其次为腹膜后和睾丸旁,少数病例位于腹股沟、精索、纵隔、胸腔和头颈部等处。
诊断要点:
1. 多发生于60岁以上的老年人,偶可发生于青少年;
2. 好发于大腿,其次为腹膜后和睾丸旁,少数病例位于腹股沟、精索、纵隔、胸腔和头颈部等处;
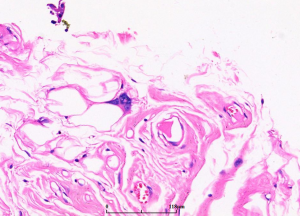
3. 肿瘤体积多较大,多结节状或分叶状,有菲薄的纤维性包膜,部分位于腹膜后者有多个大小不一的卫星结节,切面似脂肪;
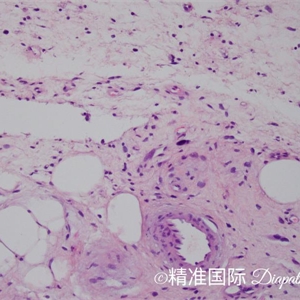
4. 根据肿瘤内的细胞组成,分为脂肪瘤样型、硬化性、梭形细胞型和炎症型四种亚型:
1)脂肪瘤样脂肪肉瘤:
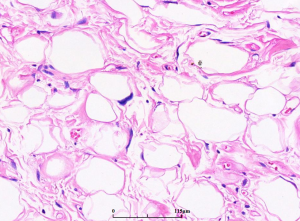
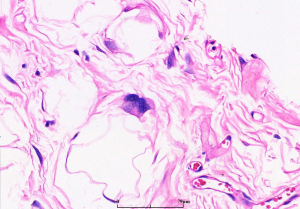
(1)主要由成熟脂肪组织和少量散在的脂肪母细胞组成,并由纤维组织分隔成大小不等的小叶;
(2)小叶内的脂肪细胞大小不一致;
(3)在纤维性分隔内可见散在的核深染、外形不规则的异型梭形细胞和畸形细胞;
(4)可见多少不等的多泡状或单泡状脂肪母细胞,可以多见,也可以极少而难以找到;
(5) 部分发生于腹膜后病例还可伴有黏液样变性,应与黏液性脂肪肉瘤鉴别;
(6)极少病例同时含有异源性成分,如化生骨等;
2) 硬化性脂肪肉瘤(sclerosing liposarcoma)
(1) 多发生于腹膜后和睾丸旁;
(2)镜下主要由致密的胶原纤维化区域组成;
(3)胶原化区域梭形细胞有一定的异型性,并可见核深染的畸形细胞,以及少量的多泡状脂肪母细胞;
(4)注意 当纤维组织占据肿瘤的绝大部分而脂肪细胞很少时,容易被误诊为其他各种类型的梭形细胞肿瘤。
3)炎症性脂肪肉瘤(inflammatory liposarcoma)
(1) 比较少见,多发生于腹膜后;
(2) 在脂肪瘤样脂肪肉瘤或硬化性脂肪肉瘤内含有数量不等的淋巴细胞和浆细胞浸润,常形成结节状的聚集灶或生发中心,有时脂肪成分可被炎症背景所掩盖。
4)梭形细胞脂肪肉瘤(spindle cell liposarcoma):由条束状排列的纤维母细胞样梭形细胞和脂肪瘤样脂肪肉瘤组成,梭形细胞在形态上无明显的异型性,间质可伴有程度不等的胶原变性或黏液样变性。
5. 注意:仅仅依靠脂肪母细胞并不能确诊为脂肪肉瘤,必须结合其他形态,因为脂肪母细胞也可以出现在脂肪母细胞瘤和软骨样脂肪瘤等一些良性的脂肪肿瘤内。
免疫组织化学染色:
分子标记:
鉴别诊断:
1、脂肪瘤 :大多数比ALT/WDLPS小,但有些可以增长到非常大的尺寸;缺乏不规则、多色、多形核的非典型间质细胞;
预后:
治疗:
参考文献:
1.Dei Tos AP: Liposarcomas: diagnostic pitfalls and new insights. Histopathology. 64(1):38-52, 2014
2.Al-Zaid T et al: Pleomorphic fibroma and dermal atypical lipomatous tumor: are they related? J Cutan Pathol. 40(4):379-84, 2013
3.Boni A et al: Atypical lipomatous tumor mimicking giant fibrovascular polyp of the esophagus: report of a case and a critical review of literature. Hum Pathol. 44(6):1165-70, 2013
4.Iwasa Y et al: Dedifferentiated liposarcoma with lipoma-like well-differentiated liposarcoma: clinicopathological study of 30 cases, with particular attention to the comingling pattern of well- and dedifferentiated components: a proposal for regrouping of the present subclassification of well-differentiated liposarcoma and dedifferentiated liposarcoma. Int J Surg Pathol. 21(1):15-21, 2013
5.Sioletic S et al: Well-differentiated and dedifferentiated liposarcomas with prominent myxoid stroma: analysis of 56 cases. Histopathology. 62(2):287-93, 2013
6.Hogg ME et al: Atypical lipomatous tumor/well-differentiated liposarcoma: what is it? Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 21(2):333-40, 2012
7.Kashima T et al: Sensitivity of MDM2 amplification and unexpected multiple faint alphoid 12 (alpha 12 satellite sequences) signals in atypical lipomatous tumor. Mod Pathol. 25(10):1384-96, 2012
8.Piperi E et al: Well-differentiated liposarcoma/atypical lipomatous tumor of the oral cavity: report of three cases and review of the literature. Head Neck Pathol. 6(3):354-63, 2012
9.Ray-Coquard I et al: Effect of the MDM2 antagonist RG7112 on the P53 pathway in patients with MDM2-amplified, well-differentiated or dedifferentiated liposarcoma: an exploratory proof-of-mechanism study. Lancet Oncol. 13(11):1133-40, 2012
10.Tseng WW et al: Lymphocyte composition and distribution in inflammatory, well-differentiated retroperitoneal liposarcoma: clues to a potential adaptive immune response and therapeutic implications. Am J Surg Pathol. 36(6):941-4, 2012